实验室在《Journal of Ethnopharmacology》发表川乌各部位代谢物分析及毒性评价的最新成果
近日,威尼斯98488药学院/现代中药产业学院、西南特色中药资源国家重点实验室彭成教授、谭玉柱副教授团队联合新加坡南洋理工大学表型组学中心王玉兰教授在国际知名期刊Journal of Ethnopharmacology(中科院分区二区,TOP期刊)发表题为Unlocking the hidden potential: Enhancing the utilization of stems and leaves through metabolite analysis and toxicity assessment of various parts of Aconitum carmichaelii的论文,周银林为第一作者,彭成教授、谭玉柱副教授及王玉兰教授为通讯作者,西南特色中药资源国家重点实验室为第一单位。
毛茛科多年生草本植物川乌(Aconitum carmichaelii Debx.)的子根(侧根)加工品为附子,其母根为乌头。附子性味辛、甘、大热,有毒,主归心、肾、脾经,是临床上常用的有毒中药,具有回阳救逆,补火助阳,散寒止痛之功,被称为“回阳救逆第一品药”。尽管附子的药用效果显著,但其毒性一直限制其临床应用。川乌作为著名的川产道地药材,目前主要使用其主根与侧根作为药用部位,而占总生物量40%的茎叶却常废弃不用。课题组前期研究显示,川乌茎叶富含阿朴啡类生物碱和醇氨型二萜类生物碱,并从中发现抗肿瘤苗头化合物(Phytochemistry 207, 113558),显示出川乌茎叶药用开发潜力巨大。然而,有关川乌各部位化学成分及毒性分析尚缺乏系统研究,这限制了川乌茎叶资源的进一步开发。
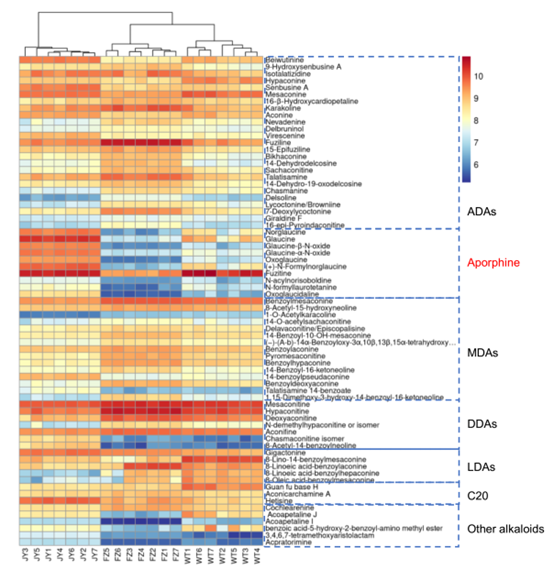
Fig. 1 The hierarchical clustering heatmap of different metabolites.
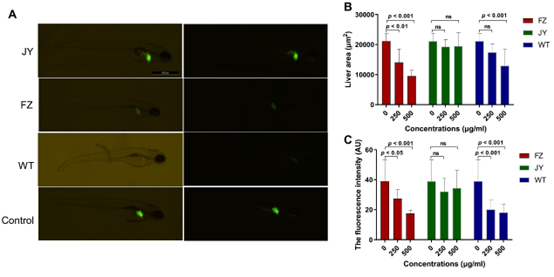
Fig. 2 (A) The effects of 500 µg/ml concentration in various parts of Aconitum carmichaelii on zebrafish liver (The scale bar is 500 µm). The effects of various parts of Aconitum carmichaelii on fabp10:EGFP zebrafish (B) liver area and (C) liver fluorescence intensity (n = 8).
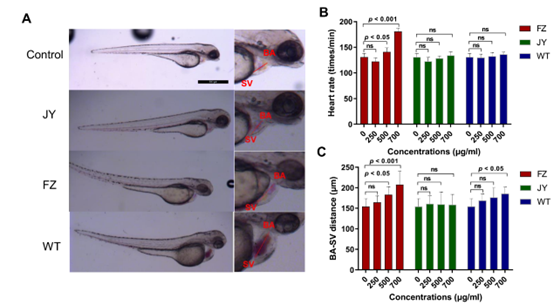
Fig. 3 (A) The effects of various parts of Aconitum carmichaelii on the BA-SV distance of zebrafish at a concentration of 500 µg/ml (The scale bar is 500 µm). The effects of extracts from various parts of Aconitum carmichaelii on (B) heart rate and (C) BA-SV distance (n ≥ 7).
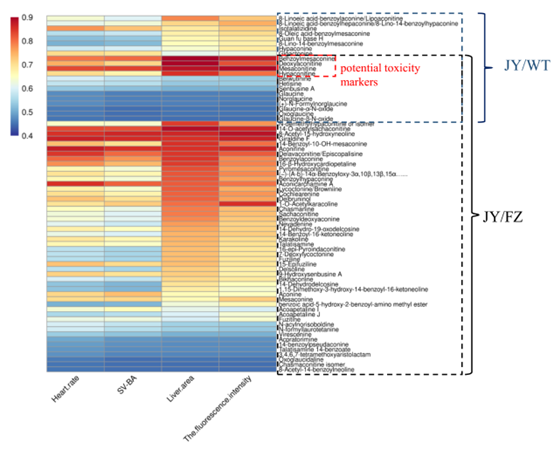
Fig. 4 Correlation coefficient heat map of the toxicity associated with differential metabolites in the JY and medicinal parts of Aconitum carmichaelii. (JY/WT, the differential metabolites of JY and WT; JY/FZ, the differential metabolites of JY and FZ.)
本研究基于植物代谢组学技术,对川乌各部位(茎叶、子根、母根)差异成分进行筛选,并从心脏毒性和肝脏毒性评价各部位毒性差异,研究其毒性标志物。本研究揭示了川乌不同部位的化学成分和毒性之间的关联,为川乌茎叶资源的开发利用提供参考。
该研究得到国家自然科学基金(82373837)、国家中医药多学科交叉创新团队(ZYYCXTD-D-202209)、四川省中医药科技产业创新团队(2022C001)及四川省杰出青年科技人才计划(2021JDJQ0040)等项目的支持。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2023.117693
供稿:西南特色中药资源国家重点实验室、威尼斯98488药学院/现代中药产业学院谭玉柱课题组。
